The Sacroiliac Joint is an Axial Joint between the bones of the Sacrum (which is a continuation of the spine) and the Ilium (part of the pelvic bones).
Only a small degree of movement, about 2-4 mm in each direction is available in the SIJ, enabling load transfer between the upper body and lower limb.
What causes Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction
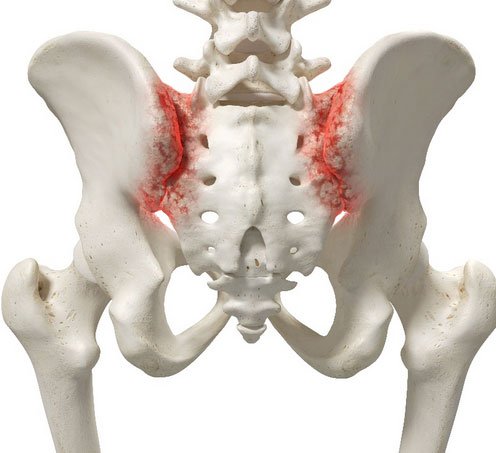
The Sacroilliac Joint
Dysfunction often occurs in the SIJ for four main reasons:
1. Inflammation- Inflammatory conditions from autoimmune disorders
2. Hormonal - During pregnancy the ligaments become lax and create excessive movement and alter the biomechanics of the joint.
3. Biomechanics- Altered forces around the SIJ due to muscle imbalances, leg length discrepancies, poor ergonomics, foot wear or repetitive and prolonged forces. Injury typically occurs in response to combined vertical forces with rapid compression.
4. Trauma- A fall onto the buttock.
SIJ pain is noted on palpation of the joint. Pain may be noted as sharp or as an ache. Activities that aggravate SIJ pain are rolling over in bed, lying on the effected side, putting on shoes, bending forward, moving into standing afer prolonged periods of lying or sitting.
Sacroiliac Joint Recommended Treatment
Treatment includes rest from the aggravating activities and activity modification, ice, and compression using an SIJ best can be very beneficial particularly for pregnant women. Taping, correct foot wear, addressing possible leg length discrepancies, and strengthening weak areas and stretching tight muscles. Techniques that may be usefull are: Dry Needling, Muscle Energy Techniques, Pilates, core training and ergonomics.
Sacroiliac Joint Recovery Time
During an acute episode recovery can take up to 2-3 weeks. Long standing chronic pain may take 3-6 months to address the underlying strength deficits and develop core control sufficient enough to positively effect pain during the aggravating activity particurly if the activity requires significant load transfer. Failure of conservative management may necessitate the use of Cortisone Injections and in desperate cases- joint fusions.
